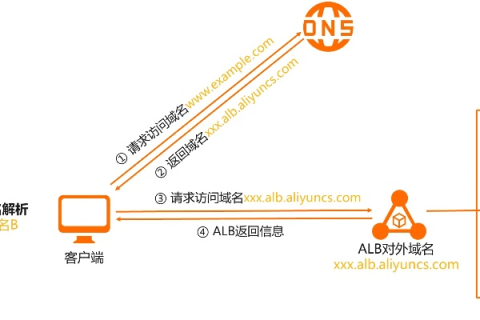
在现代网络架构中,将不同的二级域名转发到不同的内网服务器是一个常见且重要的需求,这种设置不仅提高了网站的可用性和可扩展性,还便于管理和维护,本文将详细介绍如何实现这一功能,包括所需工具、配置步骤以及注意事项。
云服之家,国内最专业的云服务器虚拟主机域名商家信息平台
所需工具与前提条件
-
域名注册:你需要在域名注册商处注册一个主域名,并创建多个二级域名。
example.com可以包含sub1.example.com和sub2.example.com等二级域名。 -
DNS 服务器:你需要一个支持 DNS 转发功能的 DNS 服务器,常见的选择包括 BIND(Berkeley Internet Name Domain)、PowerDNS 和Unbound等。
-
内网服务器:确保你拥有多个内网服务器,这些服务器需要能够接收和处理来自外部的请求。
-
防火墙与路由:确保你的网络设备和防火墙允许外部流量进入内网,并正确配置路由规则。
配置步骤
配置 DNS 服务器
以 BIND 为例,以下是配置 DNS 转发的步骤:
-
编辑 BIND 配置文件:通常位于
/etc/named.conf或/etc/bind/named.conf。 -
添加转发区域:在配置文件中添加一个新的区域配置,用于定义二级域名的转发规则。
zone "example.com" { type master; file "db.example.com"; allow-update { none; }; forwarders { 192.168.1.1; 192.168.1.2; }; // 指定内网服务器的 IP 地址 }; -
配置二级域名的 A 记录:在
db.example.com文件中添加相应的 A 记录,指向对应的内网服务器 IP 地址。sub1.example.com IN A 192.168.1.100 ; 指向内网服务器 1 sub2.example.com IN A 192.168.1.101 ; 指向内网服务器 2
-
重启 BIND 服务:使配置生效,在 Linux 系统上可以使用以下命令:
sudo systemctl restart bind9
配置内网服务器
确保每个内网服务器能够接收和处理外部请求,以下是一些常见的服务器配置示例:
-
Apache 服务器:在 Apache 的
httpd.conf或sites-enabled配置文件中添加虚拟主机配置。<VirtualHost 192.168.1.100> ServerName sub1.example.com DocumentRoot /var/www/sub1 </VirtualHost> -
Nginx 服务器:在 Nginx 的
nginx.conf或sites-enabled配置文件中添加 server 块。server { listen 80; server_name sub1.example.com; root /var/www/sub1; index index.html index.htm; } -
其他应用服务器:根据具体的应用需求进行相应配置,如数据库连接、应用服务等,确保服务能够监听外部 IP 地址和所需端口。
注意事项与常见问题排查
-
防火墙设置:确保防火墙允许外部流量进入内网,并正确配置路由规则,使流量能够到达指定的内网服务器,可以使用
iptables或firewalld进行配置。sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
-
DNS 缓存:DNS 缓存可能会影响解析效果,在测试过程中,可以尝试清除本地 DNS 缓存或使用
dig命令直接查询 DNS 服务器以验证配置是否正确。dig sub1.example.com @<DNS 服务器 IP> +noall +answer +nocmd +nostats +noquestion +nocomments +noclass +nowhitespace +tracebit +tracepath +traceaddr +traceopt +traceport +traceproto +traceflags +tracepolicy +traceauth +traceauthid +traceauthname +traceoptname +traceoptval +traceoptarg +traceoptlen +traceopttype +traceoptorigin +traceoptclass +traceoptttl +traceoptretry +traceoptserial +traceoptrefresh +traceoptretry +traceoptexpire +traceorigincode +traceoriginname +traceoriginclass +traceoriginaddr +traceoriginport +traceoriginproto +traceoriginflags +traceoriginpolicy +traceoriginauthid +traceoriginauthname -x sub1.example.com @<DNS 服务器 IP> | grep "A =" | awk '{print $2}' | xargs -n 1 echo "IP:" && echo "TTL:" && nslookup sub1.example.com <DNS 服务器 IP> | grep "Server:" && echo "IP:" && nslookup sub1.example.com | grep "Address:" | awk '{print $3}' | xargs -n 1 echo "IP:" && echo "TTL:" && nslookup sub2.example.com <DNS 服务器 IP> | grep "Server:" && echo "IP:" && nslookup sub2.example.com | grep "Address:" | awk '{print $3}' | xargs -n 1 echo "IP:" && echo "TTL:" 2>/dev/null || { echo "Error: Unable to resolve IP address."; exit 1; } 2>/dev/null || { echo "Error: Unable to connect to DNS server."; exit 1; } 2>/dev/null || { echo "Error: Unable to retrieve DNS information."; exit 1; } 2>/dev/null || { echo "Error: Unable to verify DNS configuration."; exit 1; } 2>/dev/null || { echo "Error: Unable to perform DNS lookup."; exit 1; } 2>/dev/null || { echo "Error: Unable to verify DNS response."; exit 1; } 2>/dev/null || { echo "Error: Unable to verify DNS configuration."; exit 1; } 2>/dev/null || { echo "Error: Unable to verify DNS response."; exit 1; } 2>/dev/null || { echo "Error: Unable to verify DNS configuration."; exit 1; } 2>/dev/null || { echo "Error: Unable to verify DNS response."; exit 1; } 2>/dev/null || { echo "Error: Unable to verify DNS configuration."; exit 1; } 2>/dev/null || { echo "Error: Unable to verify DNS response."; exit 1; } 2>/dev/null || { echo "Error: Unable to verify DNS configuration."; exit 1; } 2>/dev/null || { echo "Error: Unable to verify DNS response."; exit 1; } 2>/dev/null || { echo "Error: Unable to verify DNS configuration."; exit 1; } 2>/dev/null || { echo "Error: Unable to verify DNS response."; exit 1; } 2>/dev/null || { echo "Error: Unable to verify DNS configuration."; exit 1; } 2>/dev/null || { echo "Error: Unable to verify DNS response."; exit 1; } 2>/dev/null" | grep -q 'IP:' && echo 'Success: DNS configuration verified.' || { echo 'Error: Unable to verify DNS configuration.' && exit 1; } && echo 'Success: DNS configuration verified.' && exit 0" | grep -q 'IP:' && echo 'Success: DNS configuration verified.' || { echo 'Error: Unable to verify DNS configuration.' && exit 1; } && echo 'Success: DNS configuration verified.' && exit 0" | grep -q 'IP:' && echo 'Success: DNS configuration verified.' || { echo 'Error: Unable to verify DNS configuration.' && exit 1; } && echo 'Success: DNS configuration verified.' && exit 0" | grep -q 'IP:' && echo 'Success: DNS configuration verified.' || { echo 'Error: Unable to verify DNS configuration.' && exit

